W-4 Forms and Types
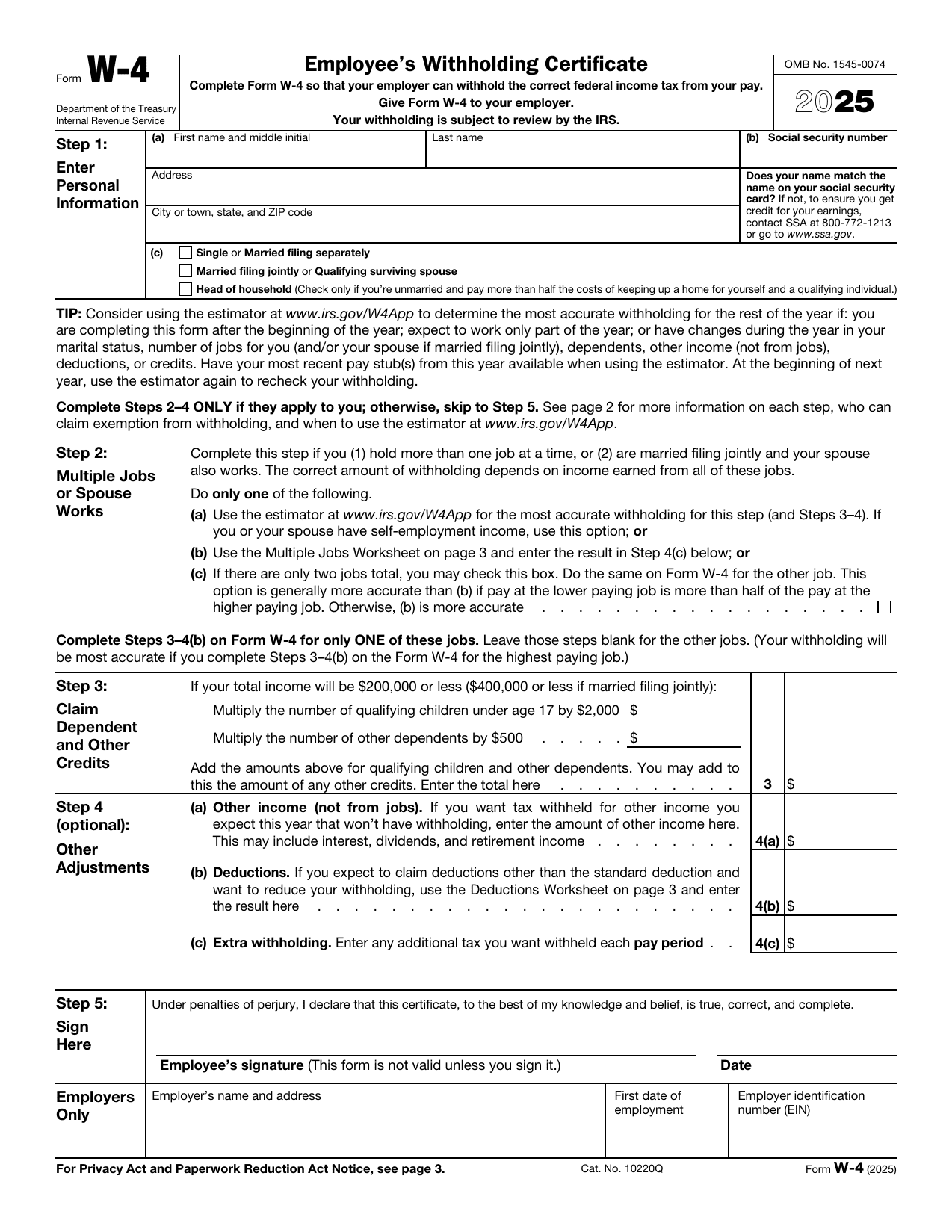
A W-4 is a tax withholding form taxpayers submit to their employer(s) to allow them to withhold the correct federal income tax from each pay period. A detailed overview of each W-4 step section is available here. You will submit a W-4 any time you take on a new job or role, even if it's just a short-term summer job, and you can submit a new one to adjust your withholding at any time.
What is a Form W-4?
How to complete a W-4?
Types of W4 Forms
W4 Tax Withholding Calculator
W-4 withholding examples
Is a Large Tax Refund a Self-Imposed Penalty?
Create, Complete your Form W-4
The question is, how do you know how to fill out a W-4? That's where we can help: here on eFile.com, you have two free options to create your W-4. The Form W4 Creator guides you through the steps to just fill out a PDF Form W-4 without additional calculations. For more tax planning purposes, use the PAYucator and enter your current or future paycheck information and your W-4 PDF Form will be created for you based on your paystub. Make adjustments over time based on your next paystub or tax return goal.
- Form W-4 Creator: Create, fill-out a Form W-4. This online tool will complete and fill-out a W-4 without any additional calculations or suggestions. Consider this option if you have an idea of what Form W-4 is and just want a quick tool to fill in the details for you.
- PAYucator based W-4: Create Form W-4 based on your paycheck. Complete and adjust your paycheck and the tool will create a Form W-4 based on your results.
eFile.com has dedicated an entire site to just calculating and creating a W-4 PDF form:
https://www.w4forms.com
Complications With Tax Withholding:
- Too Little: If a taxpayer withholds too little in federal and/or state taxes each pay period, you might owe taxes when you eFile. If your tax return shows that you owe above a certain amount (e.g. $1,000), you might face a penalty for withholding too little in taxes.
- Too Much: On the other hand, if a taxpayer withholds too much each pay period, they generally receive a federal or state tax refund. If you withhold too much in taxes, you're essentially giving your money to a tax agency as a kind of temporary loan that gets paid out as a tax refund after you file your taxes.
- Exempt: A taxpayer may claim exemption from tax withholding if the following conditions are met:
- Condition 1: They had no federal income tax liability in the previous tax year.
- Condition 2: They expect to have no federal income tax liability for the current calendar or tax year. (Think this could apply to you? Find out and estimate your income taxes).
- How do you know if you had no taxable income liability on your return for the previous tax year?
- A: Your total tax on Form 1040 for the previous tax year was zero - see line 22 page 1 on Form 1040 or less than the total of your Earned Income Tax Credit line 27, Child Tax Credit or line 28, and American Opportunity Credit line 29 on your form 1040 page 2.
- B: You were not required to file a tax return since your taxable income was below the filing threshold for your correct filing status.
- Tip about tax withholding exemption: If you claim the tax withholding exemption, you will have no income tax withheld from your paycheck and may owe taxes and penalties when you file your tax return.
- How to claim the tax withholding exemption: Make sure you meet both of the above conditions (1 and 2) by writing “Exempt” on Form W-4 in the space below Step 4(c). In addition, on Form W-4, complete Steps 1(a), 1(b), and 5. No other steps are needed. Start the eFile.com W-4 Form tool and complete your W-4 form online today!
- See more information on tax withholding and learn when you must furnish a new W-4 for tax withholding and estimated tax.
W-4 Withholding Video
Form W-4 Types
Form W-4P
Pension, Annuity Recipients
For annuity and pension payments:
view Form W-4P
Form W-4V You can use Form W-4V to ask the payer to withhold federal income taxes; this form is usually for
Social Security income recipients,
unemployment compensation recipients, are for other income which taxes are not withheld for:
- Unemployment compensation (including Railroad Unemployment Insurance Act (RUIA) payments)
- Social Security benefits
- Social Security equivalent Tier 1 railroad retirement benefits
- Commodity Credit Corporation loans
- Certain crop disaster payments under the Agricultural Act of 1949 or under Title II of the Disaster Assistance Act of 1988
- Dividends and other distributions from Alaska Native Corporations to its shareholders. Consult your payer if you’re uncertain whether your payment is eligible for voluntary withholding.
View Form W-4v
Taxpert®
Discuss your W-4 questions and goals with a Taxpert for free and we will guide you through the process:
contact us now.
Plan your withholding and/or tax returns throughout a given tax year to take control of your finances.
Use any of these tools to create, calculate, or estimate your tax withholding.
What is a tax refund? If you withhold too much in taxes per pay period, it will most likely result in a refund on your tax return. Basically, you give your money to the IRS only to get it back with your next tax return.
Note: keep your hard-earned money now, increase your paycheck now, and keep your tax refund money with each paycheck!
What if you owe taxes: if you withhold too little in IRS taxes each pay period, you might owe taxes with your next tax return. You can easily correct this by withholding more money per pay period. Unless, of course, you don't mind paying taxes as a result of your next tax return.
Note: if you withhold too little in taxes through the year, the IRS might penalize you as a result. It is important that you know where that line is.
To see how effective your tax withholding was during the year, create a free eFile.com account and prepare your tax return. Report your income forms and see how tax balanced you are.
TurboTax® is a registered trademark of Intuit, Inc.
H&R Block® is a registered trademark of HRB Innovations, Inc.